I am a Ph.D. student at the Robotics Institute, part of the School of Computer Science at Carnegie Mellon University, advised by Prof. Ralph Hollis at the Microdynamic Systems Laboratory (MSL). I work on whole-body optimal control for dynamic mobile manipulation. I use the CMU ballbot as my test platform for which I built a pair of 7DOF lightweight arms.
I obtained my M.S. in Robotics at CMU advised by Prof. Koushil Sreenath. I obtained my B.S. in Mechanical Engineering and B.S. in Aerospace Engineering with minors in Mathematics and Multidisciplinary Design from the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Research
I am interested in the intersection of mechanical design of robots and optimal non-linear control to exploit the hardware to perform highly dynamic tasks.
|
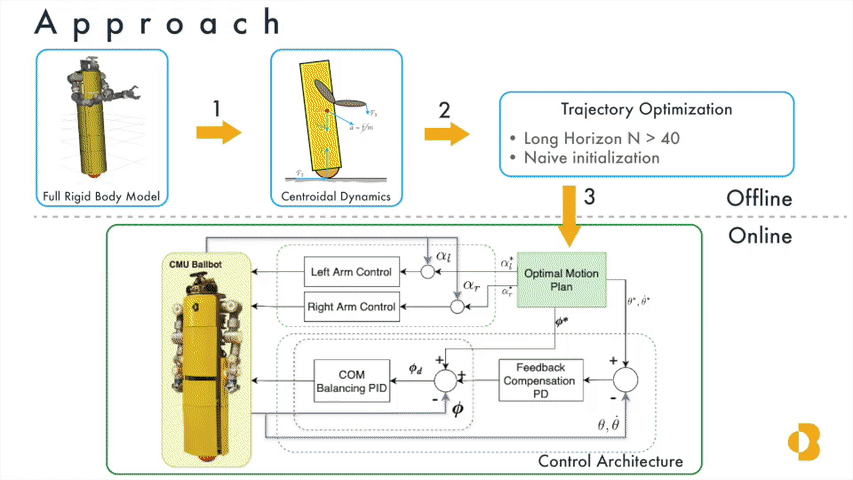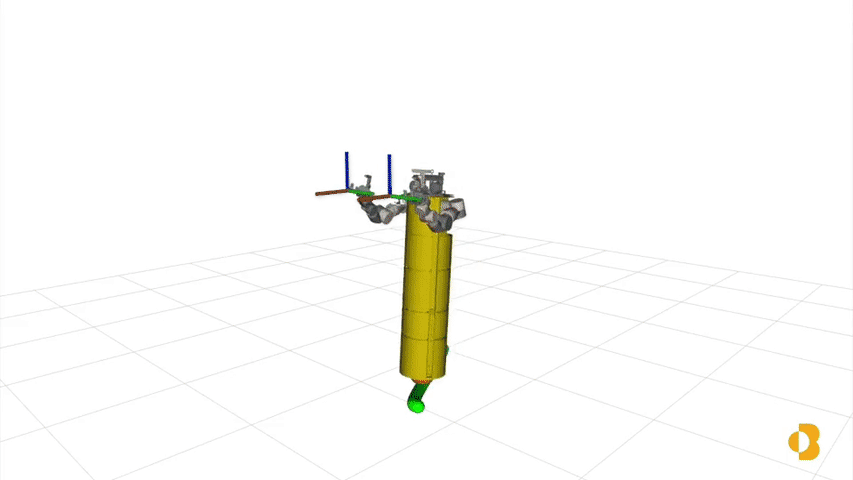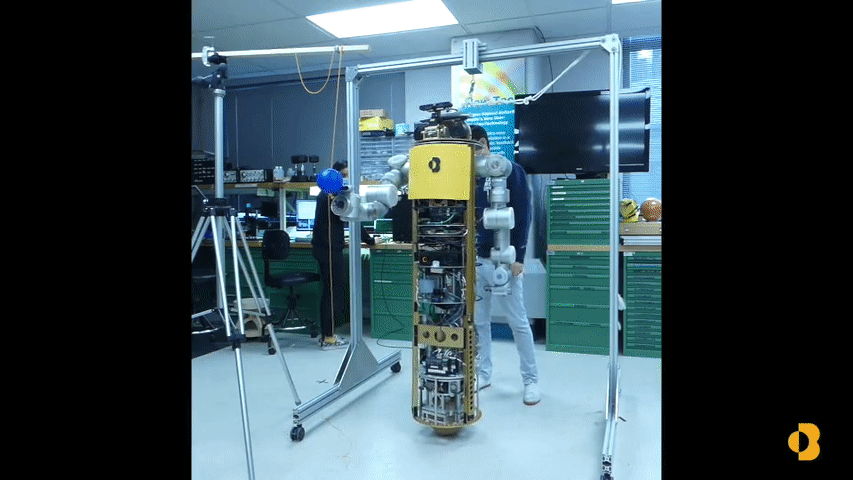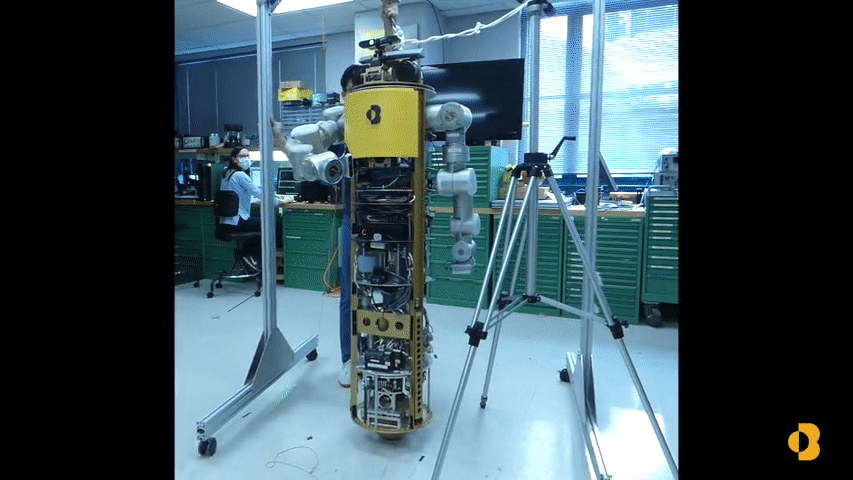
Momentum based Whole-Body Optimal Planning for a Single- Spherical-Wheeled Balancing Mobile ManipulatorRoberto Shu, Ralph Hollis 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2021 pdf / video / In this paper, we present a planning and control framework for dynamic, whole-body motions for dynamically stable shape-accelerating mobile manipulators. TWe explore the use of centroidal dynamics and trajectory optimization to generate motion plans offline that are tracked online by cascading PD-PID controllers. We demonstrate that this framework is capable of generating dynamic motion plans and control inputs with examples on the CMU ballbot. |
|
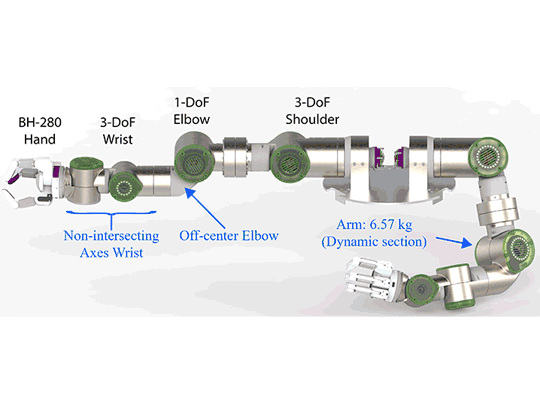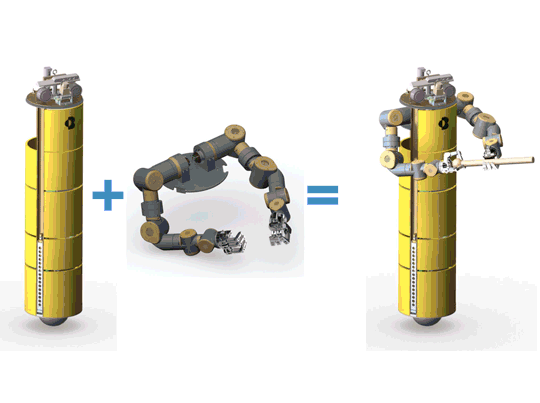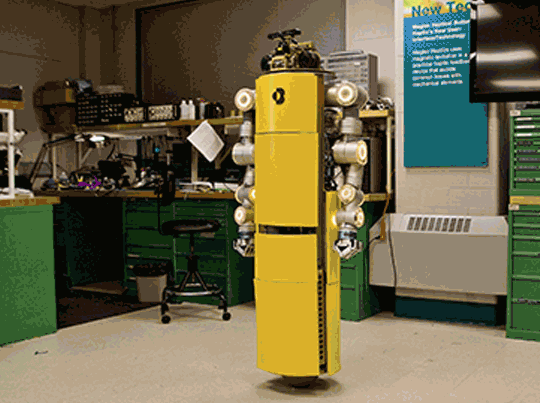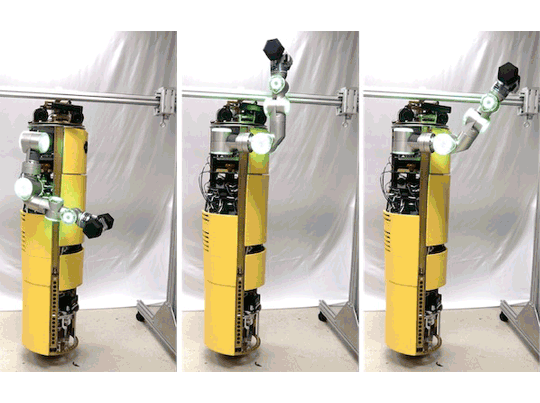
Development of a Humanoid Dual Arm System for a Single Spherical Wheeled Balancing Mobile RobotRoberto Shu, Ralph Hollis IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robotics (Humanoids), 2019 pdf / video / poster / This paper presents a new 14-DoF dual manipulation system for the CMU ballbot. The result is a new type of robot that combines smooth omnidirectional motion with the capability to interact with objects and the environment through manipulation. The system includes a pair of 7-DoF arms. Each arm weighs 12.9 kg, with a reach of 0.815 m, and a maximum payload of 10 kg at full extension. |

|
The Mechanics and Control of Leaning to Lift Heavy Objects with a Dynamically Stable Mobile RobotFabian Sonnleitner, Roberto Shu, Ralph Hollis International Conference of Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019 pdf / video / poster / A control algorithm is developed to enable dynamically stable spherical-wheel robots (ballbots) with arms to detect a heavy object of unknown mass, navigate to it, lift it, transport it, and place it in a desired location semi- autonomously. |
|
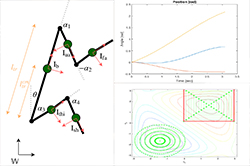
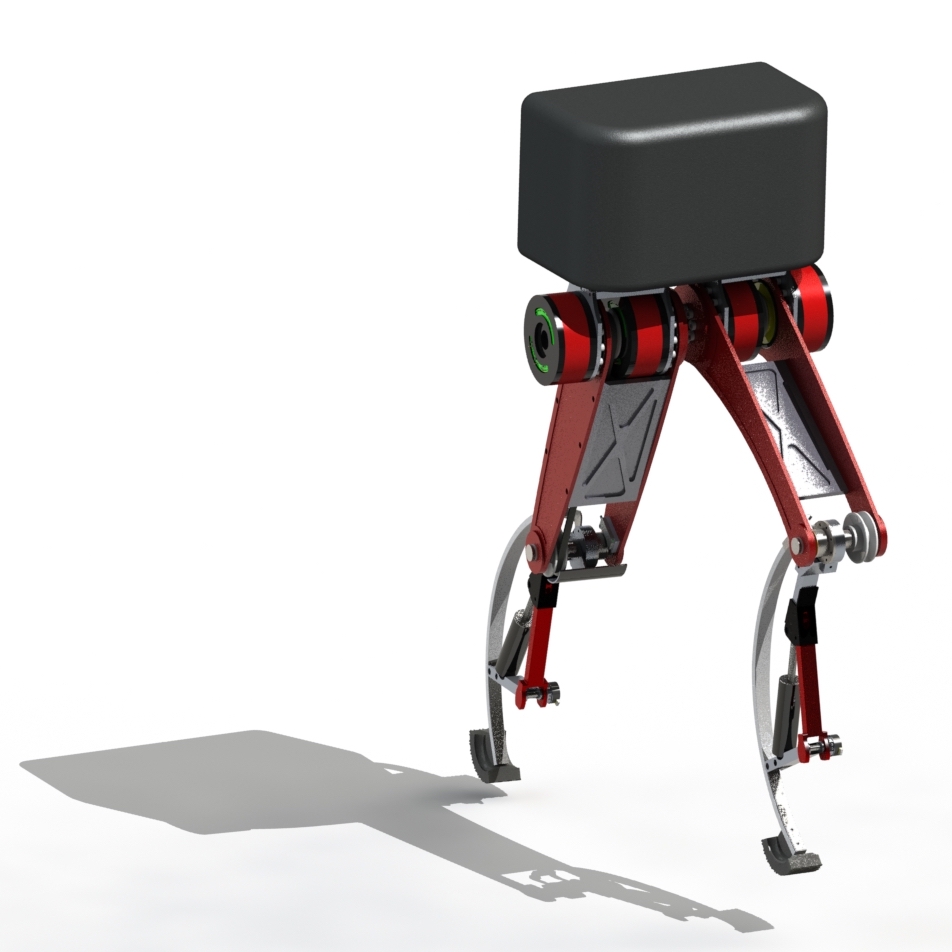
Optimal control for geometric motion planning of a robot diverRoberto Shu, Avinash Siravuru, Akshara Rai, Tony Dear, Koushil Sreenath, Howie Choset IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2016 pdf / Humans have amazing capabilites to jump of 3 story high and survive with no injuries. Legged robots are very far from realizing similar manuevers. We have designed a complete monoped to test our controller. Usually, transmission and motors are damaged due to the high impact forces. To mitigate this issue we propose a two-fold solution. |

|
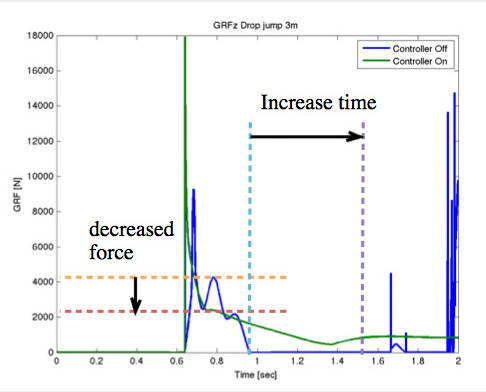
Design and Analysis of a Biped Leg to Survive High-Impact FallsRoberto Shu, Koushil Sreenath Carnegie Mellon University, 2016 pdf / Humans have amazing capabilites to jump of 3 story high and survive with no injuries. Legged robots are very far from realizing similar manuevers. We have designed a complete monoped to test our controller. Usually, transmission and motors are damaged due to the high impact forces. To mitigate this issue we propose a two-fold solution. |
|
On the utility of an active damping leg for safe landing from a free fallRoberto Shu, Avinash Siravuru, Koushil Sreenath Dynamic Walking Conference, 2015 pdf / poster / Investigate the use of a variable damping shin to dis- sipate the kinetic energy accrued from the free fall, and con- trol the leg after impact, to protect the hardware from damage. |

|
Obstacle Avoidance using Monocular VisionRoberto Shu, Hugo Ponte Carnegie Mellon University, 2014 Using Visual Words and Dictionaries desgined a guidance system that avoids obstacles in cluttered office environments using only mobile phones camera. |
|
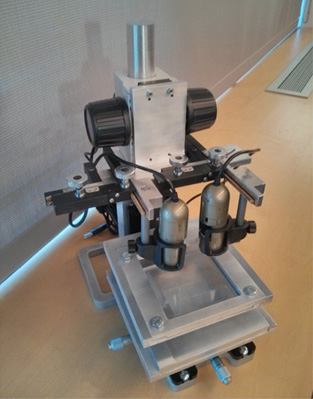
Desktop aligner for fabrication of multilayer microfluidic devicesXiang Li, Zeta Tak For Yu, Dalton Geraldo, Shinuo Weng, Nitesh Alve, Wu Dun, Akshay Kini, Karan Patel, Roberto Shu, Feng Zhang, Gang Li, Qinghui Jin, and Jianping Fu University of Michigan - Ann Arbor, 2013 pdf / poster / Accurate alignment of structure features on different PDMS layers before their permanent bonding is critical in determining the yield and quality of assembled multilayer microfluidic devices. Herein, we report a custom-built desktop aligner capable of both local and global alignments of PDMS layers covering a broad size range. Both local and global alignment accuracies of the desktop aligner were determined to be about 20 microns. |

|
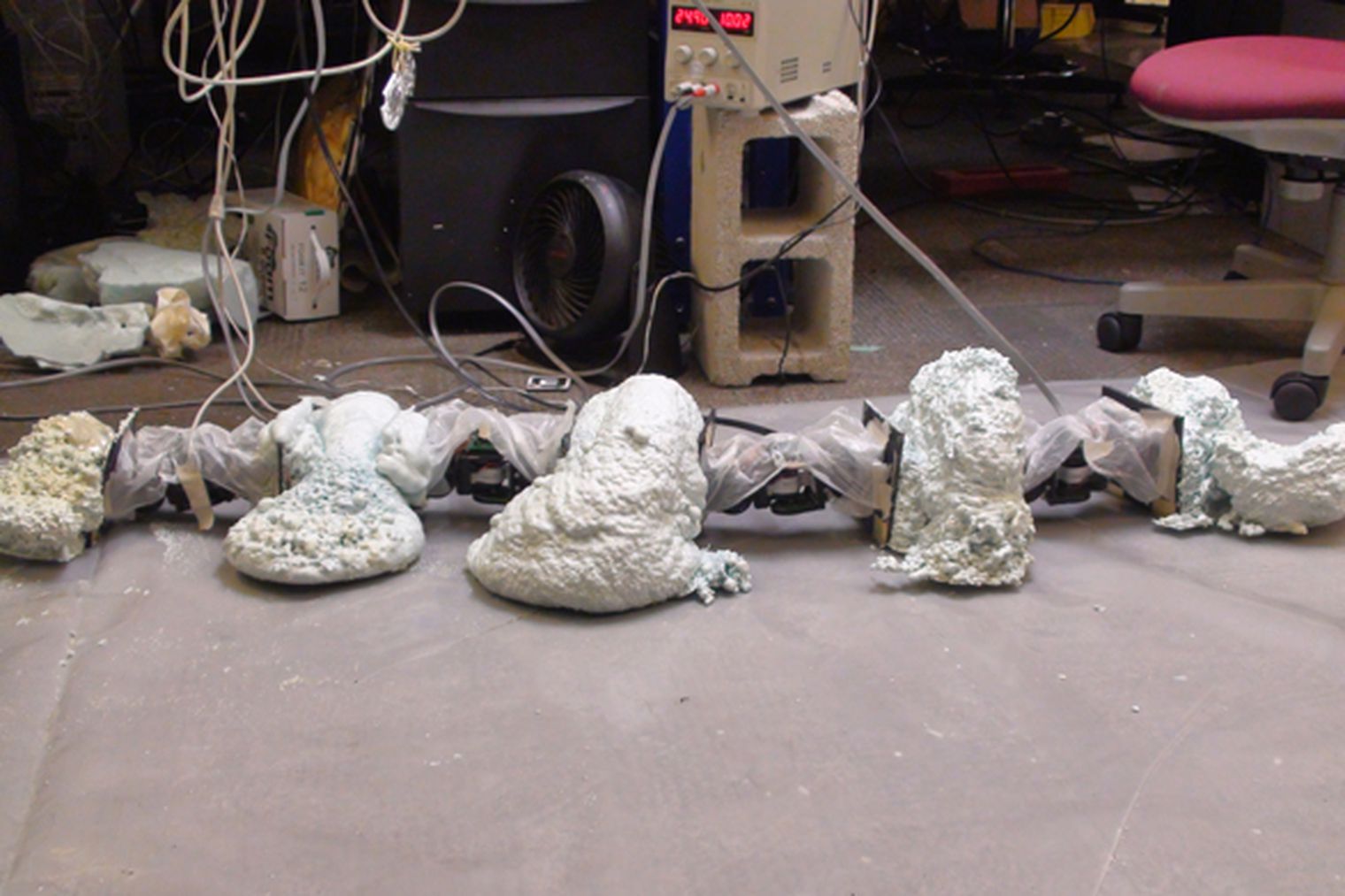
FoamBot - a modular robotics system that utilizes foam to build and reshape new robot bodies.Roberto Shu, Shai Revzen University of Michigan - Ann Arbor, 2013 video / FoamBot is a robot that assembles itself by combining modular robot components (CKBot modules) and casting foam that hardens to form the body. It consist of a main building robot that configures the CKBot modules into position and sprays the casting foam over it. When the foam cures the new robot will be able to move independently. |
Other projects

|
Estratos Ecuador - 1st Ecuadorian Flag in the StratosphereRoberto Shu, Juan Felipe Bages , 2015 video / poster / The team of “Proyecto Estratos Ecuador” (Project Stratos Ecuador in english) launched the 1st Ecuadorian Flag to the Stratosphere using a High Altitude Balloon. The ballon reach a maximum altitude of 88K feet. Telemetry and video data was retrieve successfully. Project was featured in several news feeds in Ecuador. |
|
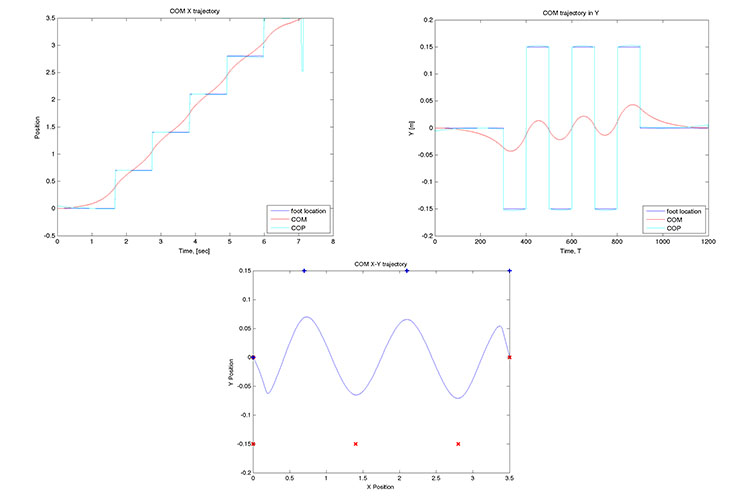
Bipedal Center of Mass Trajectory Optimization using LIPMRoberto Shu, Javier Chauvin , 2015 code / This project explores trajectory optimization. Given a set of footstep locations and timing, we find an appropriate center of mass trajectory for a bipedal robot. We use a simplified model, the linear inverted pendulum model (LIPM). |
|
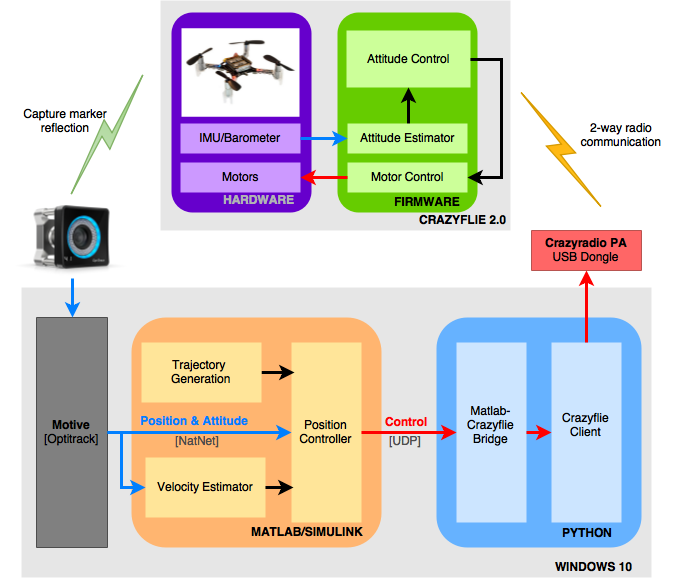
Crazyflie NanoQuadcopters matlab clientRoberto Shu, Koushil Sreenath Carnegie Mellon University, 2015 code / Crazyflie is a open source nano quadcopters. There were no ative Matlab(MEX) & Simulink clients to control the quadocpter. Commonly Matlab/Simulink is used to develop closed loop controllers. Thus, before this client it was required to communicate between different programming lannguages (python and matlab) introducing delay times. This project address this delays by creatinges a native matlab client. Deeveloped a cartesian space position tracking controller around it. |
|
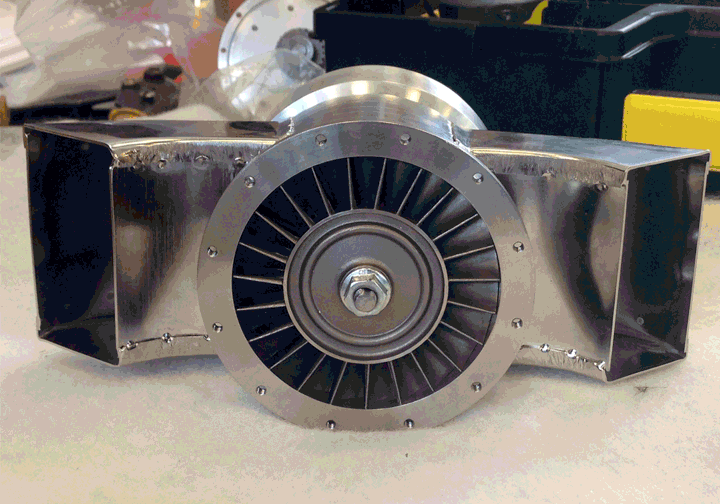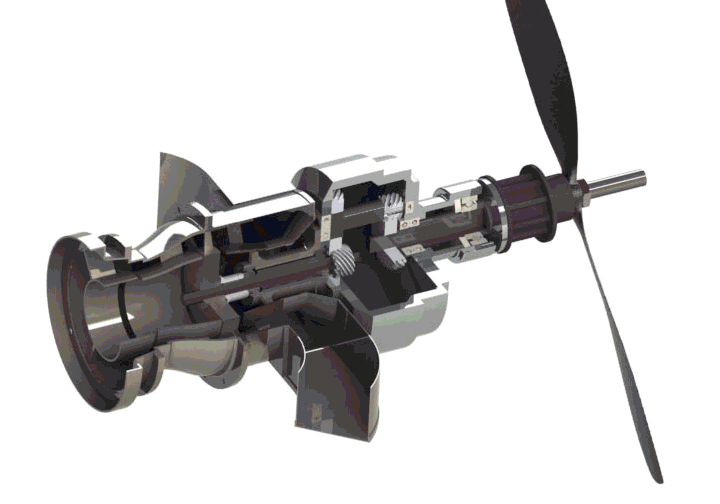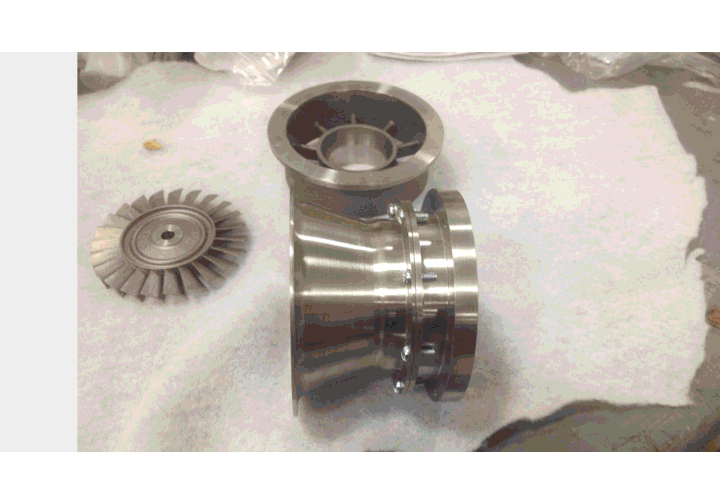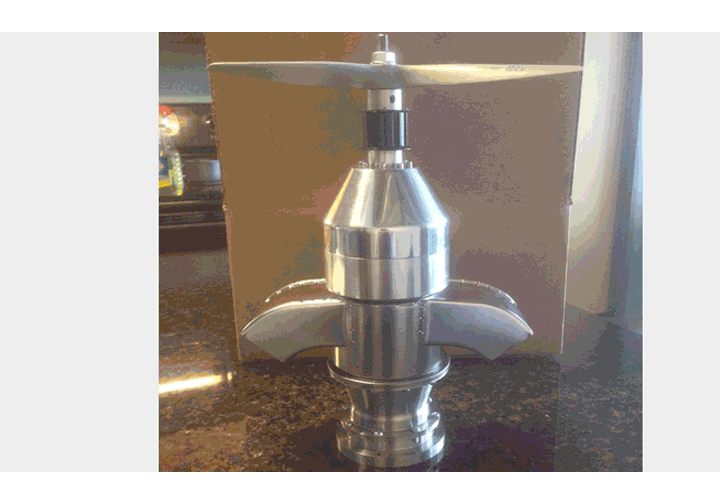
GenJet - Turboprop Add-on to Jet Engine for Electrical Power GenerationVictor Bensoussan, Christopher Labadie, Shubhankar Mohan, Roberto Shu University of Michigan - Ann Arbor, 2014 pdf / poster / Extracted 500 Wats of DC Electrical Power at 24V from a JetCat P-80SE gas turbine while mainting the stock thrust for 2013-2014 Air Force Research Laboratory Aerospace Propulsion Outreach Program competition. |
|
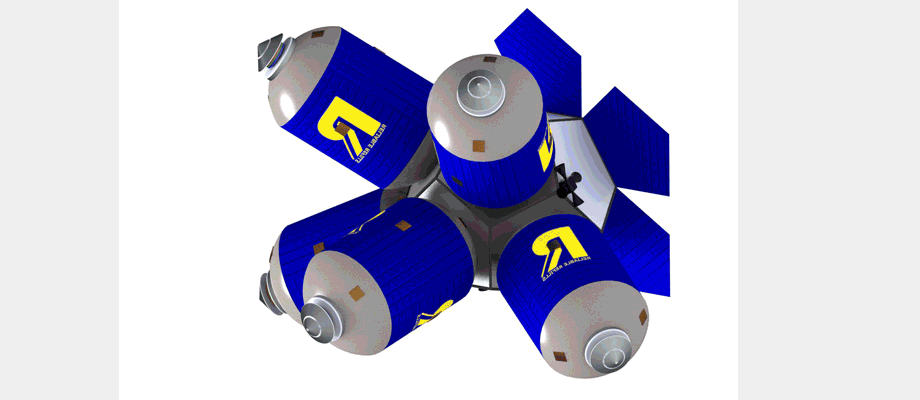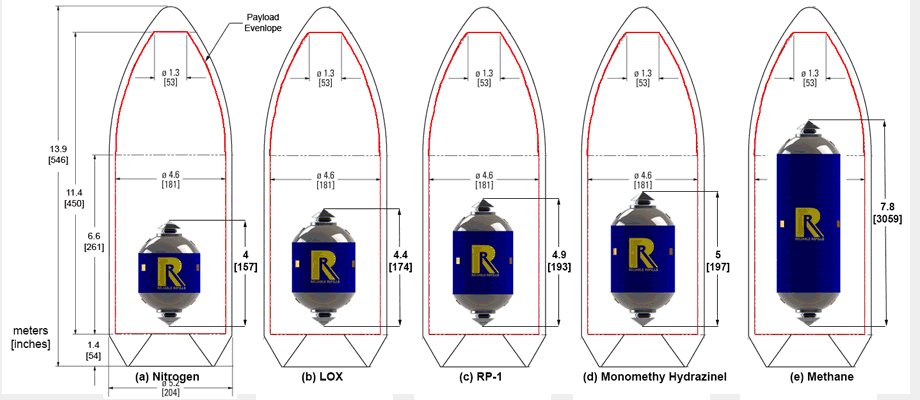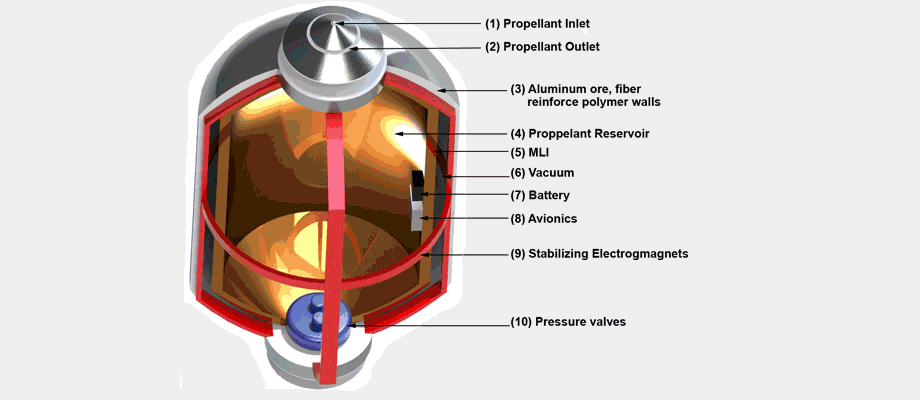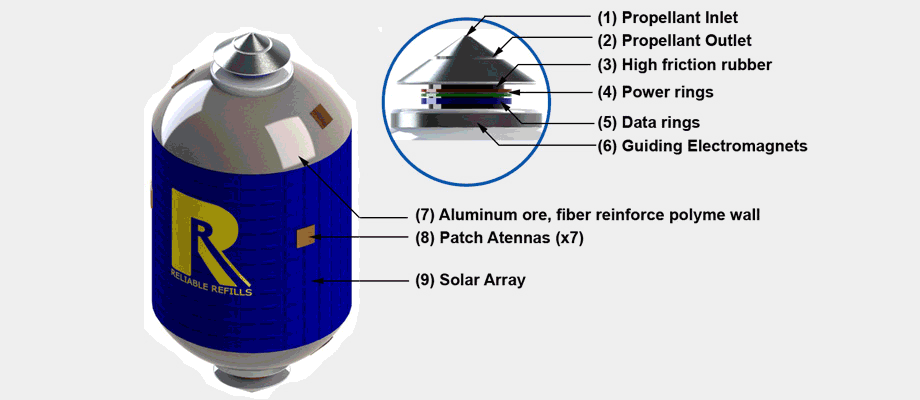
Commercial Heavy-lift Orbital Refueling DepotDavid Hash, Miles Justice, Matthew Karashin, Colin McNally, Duncan Miller, Tomasz Nielsen, Isacc Olson, Hrishikesh Shelar, Roberto Shu, Joshua Weiss, Shawn Wetherhold University of Michigan - Ann Arbor, 2013 pdf / Designed the hardware achitecture for a feasible orbital refueling station for deep space missions. Engineered fuel tanks, fuel tank hubs, docking, and refuelling system. |
Talks & Demos
Ballbot: A single-wheeled balancing robotRoberto Shu, Ralph Hollis"Carnegie Colloquium on Digital Governance and Security - Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2016 |
|
Building a Robotic Leg for High Impact LandingRoberto ShuBipedal Locomotion Seminar - Carnegie Mellon University, 2016 |
